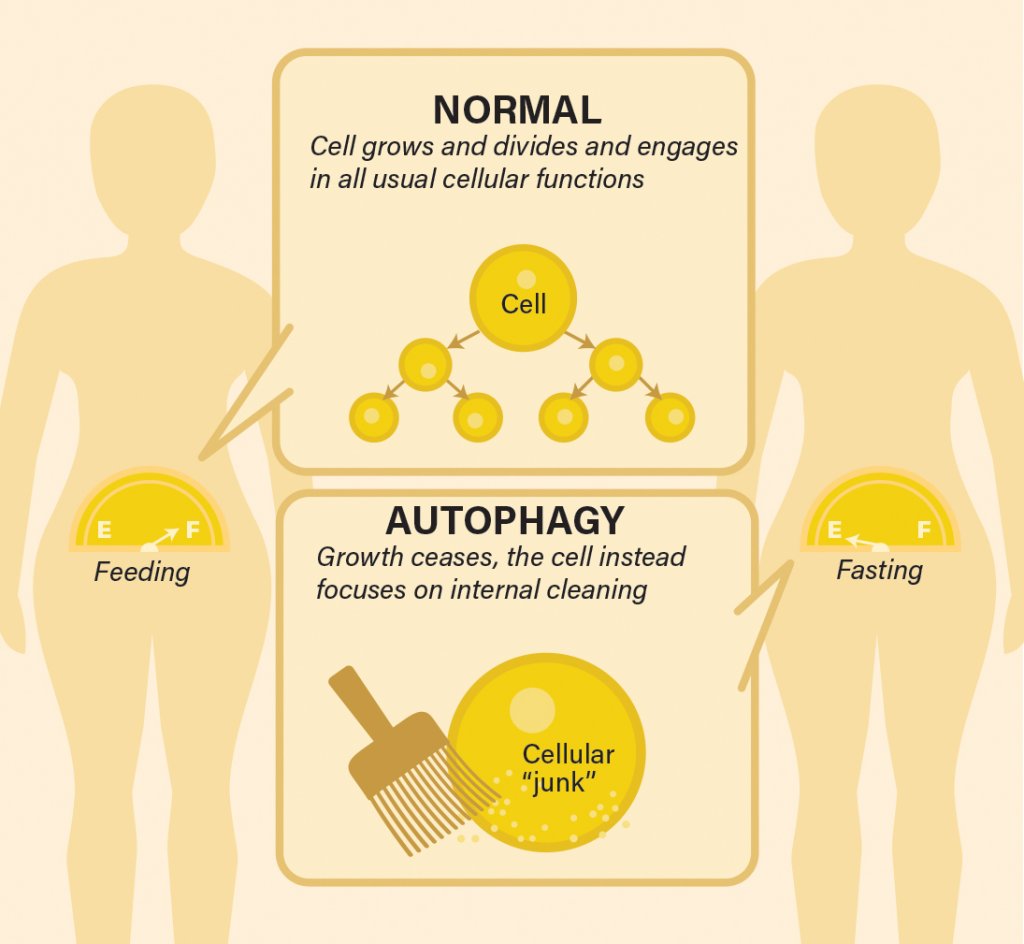
Key Takeaways A1 vs A2 Beta-Casein 🥛: A1 β-casein contains histidine at position 67, producing BCM-7 during digestion; A2 has proline and does not form BCM-7 Inflammatory Potential: BCM-7 from A1 protein may induce gut inflammation through opioid receptor activation and NF-κB pathway, potentially exacerbating autoimmune conditions Molecular Mimicry Risk: BCM-7 might mimic human peptides, leading to immune responses against self-tissues—a mechanism seen in some autoimmune diseases Gut Permeability: A1-derived BCM-7 could compromise gut barrier function ("leaky gut"), enhancing systemic exposure and influencing immune pathways A2 Milk Alternative: A2 β-casein may promote gut health by avoiding BCM-7 formation; found in Jersey cows, goats, and A2-specific milk products Considerations: Evidence emerging from animal studies and observational human data; individuals experiencing dairy-related inflammation may benefit from switching to A2-predominant sources Cow's milk, a nutritional cornerstone for many, contains proteins that have varying effects on human health. The focus here is on β-casein, specifically the A1 and A2 variants, and their potential to influence auto-immune responses and gut health.
...