Table of Contents
Investigation Protocol: Every claim is tied to primary sources including regulator emails, peer-reviewed studies, manufacturer patents, and laboratory data. Quantitative values preserve original units and methodological caveats.
Executive Summary: Beyond Contamination to Biological Threat
- 8 independent laboratories across 4 continents have confirmed plasmid DNA contamination in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
- SV40 promoter/enhancer sequences present in all positive samples, with some lots exceeding regulatory DNA limits by 500-fold
- Health Canada internal emails reveal regulatory crisis: Pfizer admitted unexpected SV40 finding, officials noted "SV40 must be avoided!" and sought to "remedy the situation before Fall 2024"
- New biological mechanism identified: SV40 enhancer disrupts somatic hypermutation - the core process of antibody diversity creation
- Manufacturer prior knowledge: Moderna's 2013 patents explicitly warn DNA fragments "may cause a patient to develop cancer" and can be "inherited by offspring"
- Regulatory transparency failure: No public comparability data for Process 1 vs Process 2; safety comparison cohort removed from trials
The Global Scientific Consensus Emerges
Between February 2023 and December 2024, eight independent research groups across North America, Europe, and Asia reported identical findings: mRNA COVID-19 vaccine vials contain residual plasmid DNA with functional SV40 promoter/enhancer sequences.
The convergence of evidence across methodologies and continents represents one of the most significant pharmaceutical quality control discoveries in modern history.
Laboratory Findings at a Glance
| Research Team | DNA Concentration Range | SV40 Confirmed | Key Finding |
|---|---|---|---|
| McKernan (USA) | 10-843 ng/dose | Yes | First discovery; shotgun sequencing |
| Buckhaults (USA) | 1-6 ng/dose | Yes | Legislative testimony; oncogenic concern |
| König/Kirchner (Germany) | 3,600-5,340 ng/dose | Yes | 500x over limit; Expression of Concern issued |
| Speicher et al. (International) | 0.22-510 ng/dose | Yes | 27+ vial analysis; lot variability |
| Raoult (France) | 2,712-5,160 ng/dose | Yes | Full plasmid recovery |
| Kämmerer (Germany) | 33-43 ng/dose in LNPs | Yes | LNP-mediated cellular delivery |
| Wang/Kim (USA) | Plasmid detected | Yes | High-school replication project |
All measurements normalized to 0.3 mL dose where applicable; methodologies vary
The Discovery That Changed Everything
In February 2023, Kevin McKernan, a genomics researcher with decades of experience in DNA sequencing, made an unexpected discovery while testing mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. What he found would trigger a global investigation and raise fundamental questions about vaccine safety and regulatory oversight.
McKernan's analysis revealed the presence of plasmid DNA fragments containing SV40 sequences - genetic material that shouldn't have been in the finished vaccine products. This wasn't just trace contamination. In some cases, the DNA levels were hundreds of times higher than established safety limits.
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated. For decades, regulatory agencies worldwide have maintained strict guidelines about DNA contamination in biological products. The International Council for Harmonisation sets the acceptable limit at just 10 nanograms per dose. Multiple independent laboratories would later find levels far exceeding this benchmark.
The RNA:DNA Hybrid Mechanism: Why DNA Persists Despite "Purification"
The fundamental reason DNA contamination persists in mRNA vaccines is a molecular biology phenomenon that manufacturers failed to address: RNA:DNA hybrids resist standard DNase I digestion.
The Hybrid Formation Process
During in vitro transcription (IVT) - the manufacturing process where mRNA is copied from DNA templates - the newly synthesized mRNA doesn't fully separate from its DNA template. Instead, it forms RNA:DNA hybrid structures where mRNA strands remain bound to the DNA plasmid.
Why Standard Clean-Up Failed
The DNase I Problem:
- Standard purification uses DNase I enzyme to degrade residual DNA
- DNase I activity on RNA:DNA hybrids is 100-fold lower than on regular double-stranded DNA (Sutton et al., 1997, PMID: 9345303)
- N1-methylpseudouridine modifications in therapeutic mRNA further stabilize these hybrids
The Selective Protection Effect:
- Hybrid-protected regions: Spike gene ORF (where mRNA binds DNA) - RESISTS DNASE I
- Non-hybridized regions: Kanamycin resistance gene, origin of replication - DEGRADED BY DNASE I
The Regulatory Assay Blind Spot
This creates a perfect storm for regulatory detection failure:
- Manufacturers test only the kanamycin resistance gene with qPCR (assuming it represents total DNA)
- Kanamycin gene shows low levels because it's degraded by DNase I
- Regulators see "acceptable" levels and approve the batch
- Hidden contamination persists in the spike gene region protected by hybrids
Key Paper: McKernan et al. (2025) demonstrated this mechanism across 5 recent vaccine lots, showing ΔCt values of 6-15 between spike and kanamycin assays - representing 100-1000-fold more DNA than regulators detected.
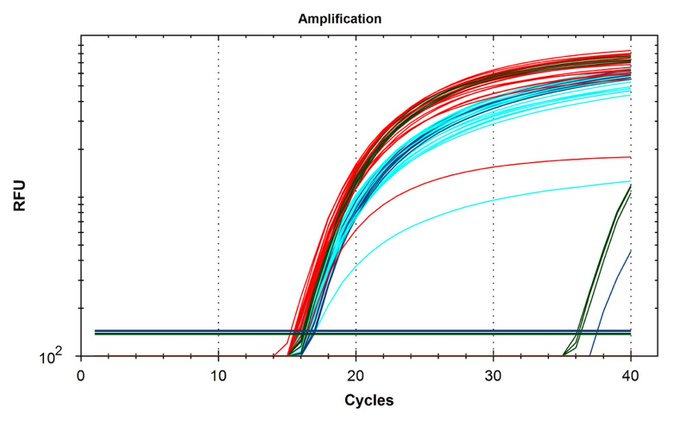 Source: Kevin McKernan, X.com (@Kevin_McKernan), 2024 - qPCR analysis showing Ct values for spike gene (left) vs kanamycin resistance gene (right) in vaccine samples
Source: Kevin McKernan, X.com (@Kevin_McKernan), 2024 - qPCR analysis showing Ct values for spike gene (left) vs kanamycin resistance gene (right) in vaccine samples
The Solution That Wasn't Used
DNase I-XT (an enhanced enzyme cocktail) can effectively degrade RNA:DNA hybrids:
- Reduces DNA levels by 100-1000x compared to standard DNase I
- Shifts spike qPCR Ct values by 10-15 cycles
- Recommended for mRNA manufacturing but not implemented by Pfizer/Moderna
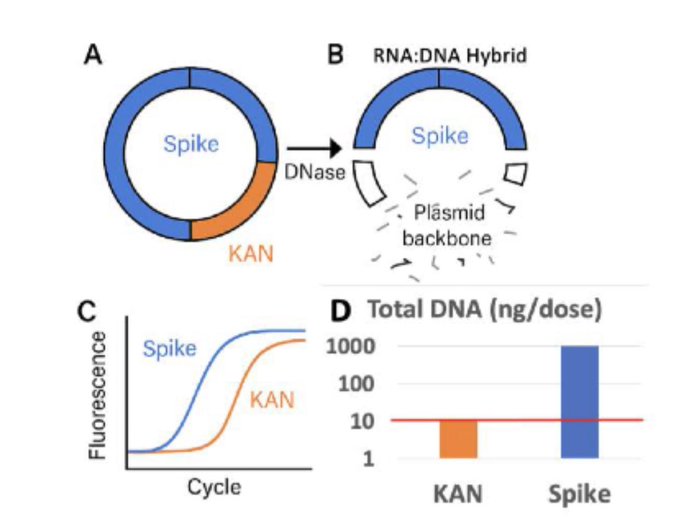 Source: McKernan et al., Zenodo (2025), doi:10.5281/zenodo.17832183 - Bar graph comparing DNA levels after treatment with standard DNase I vs DNase I-XT
Source: McKernan et al., Zenodo (2025), doi:10.5281/zenodo.17832183 - Bar graph comparing DNA levels after treatment with standard DNase I vs DNase I-XT
Implications for All Reported Findings
This hybrid mechanism explains:
- Why fluorometry shows 100x more DNA than qPCR (fluorometry detects all DNA after RNase treatment)
- Why spike gene persists while kanamycin gene is degraded
- Why SV40 promoters survive (located in protected regions)
- Why regulatory tests passed while contamination remained severe
Additional Evidence: Jessica Rose's analysis demonstrates that RNA/DNA hybrids resist enzymatic digestion, extending the biological half-life of contaminants beyond what standard degradation assays predict. This has implications for how long these fragments may remain active in the body.
Kevin McKernan: The Initial Discovery
Source: McKernan K. Sequencing of bivalent Moderna and Pfizer mRNA vaccines reveals nanogram to microgram quantities of expression vector dsDNA per dose. OSF Preprint, 2023. doi:10.31219/osf.io/b9t7m
The Finding That Started It All:
- DNA Quantification: qPCR estimates 10–60 ng/dose; fluorometry detected up to 843 ng/dose in some batches
- SV40 Confirmation: Shotgun sequencing identified complete SV40 promoter/enhancer and origin of replication
- Risk Assessment: Highlighted potential for episomal persistence and genomic integration
- Impact: Triggered global replication attempts and regulatory inquiries
Phillip Buckhaults: Legislative Alarm
Source: Buckhaults P. South Carolina Senate Medical Affairs Committee Testimony on Pfizer mRNA DNA contamination. Sept 12 2023. Official transcript
Public Accountability:
- Findings: 1–6 ng/dose with SV40 promoter/enhancer confirmation
- Risk Warning: "There is a very real hazard" of the oncogenic promoter in gene therapy contexts
- Integration Status: Not demonstrated in patient samples; exploratory tests only
- Call to Action: Urged manufacturing audits and GMP replication
Additional Laboratory Confirmations
Brigitte König & Jürgen O. Kirchner - Germany
Background: Independent laboratory analysts When: September 2023 What they found: Their analysis revealed the highest contamination levels found to date - 3,600-5,340 ng/dose, representing 360-534 times the regulatory limit. They also confirmed the presence of SV40 promoter sequences. Why it matters: These extraordinarily high contamination levels represent a serious manufacturing quality control failure. Research findings: Published in Methods and Protocols
David Speicher - Canada
Background: Researcher at University of Guelph When: October 2023 (Ontario), March 2024 (Australia) What he found: Analyzed over 27 vials from different regions and found DNA contamination ranging from 0.22 to 510 ng/dose. His work established a dose-response correlation with reported adverse events. Why it matters: Speicher's large-scale analysis across multiple lots and regions provides valuable data about contamination variability. Comprehensive reports: Ontario analysis | Australian investigation
Didier Raoult - France
Background: Renowned microbiologist and former professor at Aix-Marseille University When: November 2024 What he found: Using advanced fluorometry and sequencing, Raoult detected 2,712-5,160 ng/dose of complete plasmid DNA including full SV40 promoter/enhancer sequences. Why it matters: Raoult is one of the most cited microbiologists in the world. His involvement brought significant attention to these findings within the European scientific community. Study publication: Available through HAL Science Archive
Ulrike Kämmerer - Germany
Background: Biologist at University Hospital of Würzburg When: December 2024 What she found: Documented 32.7-43.4 ng/dose of DNA contamination within lipid nanoparticles and confirmed SV40 promoter sequences. Importantly, she demonstrated that this contaminated material could successfully transfect cells and produce spike protein. Why it matters: Her cellular transfection experiments demonstrate that the contaminated DNA is biologically active and can express genetic material in human cells. Research publication: Available on ResearchGate - Archived
 Source: Kevin McKernan, Laboratory analysis (2024) - Agarose gel electrophoresis showing DNA fragments (~5.3 kb) in mRNA vaccine samples. Lane 1: DNA ladder, Lane 2-4: Various vaccine lots, Lane 5: Negative control
Source: Kevin McKernan, Laboratory analysis (2024) - Agarose gel electrophoresis showing DNA fragments (~5.3 kb) in mRNA vaccine samples. Lane 1: DNA ladder, Lane 2-4: Various vaccine lots, Lane 5: Negative control
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated. For decades, regulatory agencies worldwide have maintained strict guidelines about DNA contamination in biological products. The International Council for Harmonisation sets the acceptable limit at just 10 nanograms per dose. Multiple independent laboratories would later find levels far exceeding this benchmark.
What started as routine quality control quickly evolved into one of the most comprehensive independent investigations in pharmaceutical history. Scientists across multiple continents began examining vaccine vials, each finding similar contamination patterns. What emerged was not just evidence of manufacturing problems, but a systematic failure of the regulatory systems designed to protect public health.
Health Canada's Internal Crisis: The Regulatory Smoking Gun
Internal emails obtained through investigative work by Scoops McGoo reveal a regulatory crisis concealed from public view:
The Unplanned Discovery
- Pfizer's Admission: "Yes, because Pfizer did not identify the presence of SV40 promoter enhancer on the plasmid template used to produce mRNA" (Email Pg. 235)
- Process 2 Connection: This admission directly implicates the commercial manufacturing process where quality controls failed

Regulatory Alarm Bells
- "SV40 must be avoided!" (Email Pg. 66) - Clear safety principle violation
- "Remedy the situation before Fall 2024 vax campaign" (Pg. 141) - Urgent timeline for Process 2 resolution
- "They do not seem to care much at this moment" (Pg. 151) - Frustration with Pfizer's response


Scientific Concern
- "Fragment size is related to the probability of integration" (Pg. 205) - fragment size is related to the probability of integration with the human genome
- "References: None" beside "minimal safety risk" claim (Pg. 203) - Unsubstantiated safety assurance minimal safety risk … "References: None"


The Manufacturing Change: Process 1 vs Process 2
The Unannounced Transition
- Process 1: Clinical trial material used for safety/efficacy authorization
- Process 2: Commercial scale-up with different purification, enzymes, and DNA template production
- Critical Question: Were they actually the same product?
The Missing Safety Comparison
- Original Protocol: Included Process 1 vs Process 2 comparison cohort
- Amendment 20 (Sept 2022): Removed the comparative objective as Process 2 dominated supply (Archive Link)
- Current Status: No public data demonstrating manufacturing equivalence
FOI Revelations
UK MHRA's response to FOI 23/510 acknowledged the comparability question but released no analytical dossier, maintaining the transparency vacuum.
For detailed analysis of manufacturing changes and their implications, see Pfizer Process 1 vs Process 2: What Changed, What's Measured, and What Remains Uncertain
Two Different Manufacturing Processes
Understanding the DNA contamination story requires knowing about two different manufacturing methods used for mRNA vaccines.
Process 1: The Clinical Trial Version
When mRNA vaccines went through clinical trials, they were produced using "Process 1." This method followed established pharmaceutical manufacturing practices and was the version tested for safety and efficacy in human trials.
Process 2: The Global Rollout Version
When vaccines were distributed to billions worldwide, manufacturers switched to "Process 2" without public announcement. This change was significant because Process 2 used different materials and methods that would later be found to produce higher levels of DNA contamination.
The Missing Safety Comparison
Critical to this story is what happened in September 2022. Pfizer's original clinical trial protocol included a plan to compare Process 1 and Process 2 directly - a standard safety requirement when changing manufacturing methods. However, Protocol Amendment 20 removed this comparison (Archive Link).
This removal meant that no formal safety comparison would ever be conducted or published. The public would never know whether Process 2 was as safe as the Process 1 version used in clinical trials.
Regulatory Silence
When researchers and citizens asked regulatory agencies for evidence proving the two processes were equivalent, they encountered repeated refusals. The UK's MHRA acknowledged receiving these requests (MHRA FOI 23/510) but provided no analytical data comparing the two manufacturing methods.
For detailed analysis of manufacturing changes and their implications, see Pfizer Process 1 vs Process 2: What Changed, What's Measured, and What Remains Uncertain
The Somatic Hypermutation Threat: Immune System Sabotage
A January 2024 preprint reveals the most concerning mechanism yet: SV40 enhancer functions as a somatic hypermutation targeting element (bioRxiv).
Understanding the Mechanism
- Somatic Hypermutation (SHM): Process where B-cells "fine-tune" antibodies for better pathogen recognition
- AID Enzyme: "Master catalyst" that enables antibody diversity through targeted mutation
- SV40 Hijacking: Can redirect SHM machinery, potentially causing:
What is Somatic Hypermutation?
Somatic hypermutation (SHM) is a natural biological process that's essential for healthy immune function. Here's how it works:
- B-cells are white blood cells that produce antibodies to fight infections
- When B-cells encounter new pathogens, they undergo SHM to fine-tune their antibodies
- This process creates antibody diversity, allowing our immune system to recognize millions of different pathogens
- The AID enzyme (Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase) acts as the "master catalyst" for this process
The SV40 Concern
The research suggests that SV40 enhancer sequences might redirect or dysregulate this natural mutation process. Instead of the normal, controlled antibody refinement, SV40 could cause:
Potential Consequences:
- Impaired Antibody Production: If SHM doesn't work correctly, the immune system might not be able to produce effective antibodies against new infections
- Unexpected DNA Mutations: If the mutation process goes awry, it could potentially affect other parts of the genome
- Autoimmune Issues: Misdirected hypermutation could theoretically contribute to autoimmune conditions
Why This Matters Scientifically
As immunologist Jessica Rose summarizes: "If we have impaired antibody responses, we have a broken immune system."
The concern isn't that SV40 definitely causes these problems, but that introducing a powerful genetic enhancer sequence into the body creates theoretical risks that deserve thorough investigation.
Manufacturer Prior Knowledge: The Moderna Patents
Moderna's own intellectual property reveals they understood the risks years before COVID-19:
Explicit Warnings in Patent Documentation
- "DNA fragments resulting from the mRNA production process need to be removed"
- "Because the remaining DNA fragments may cause a patient to develop cancer"
- "qPCR can't measure small DNA fragments, yet we have to use another method to quantify them"
- "Some of the introduced DNA may be incorporated into the genome of the cell and inherited by the offspring"
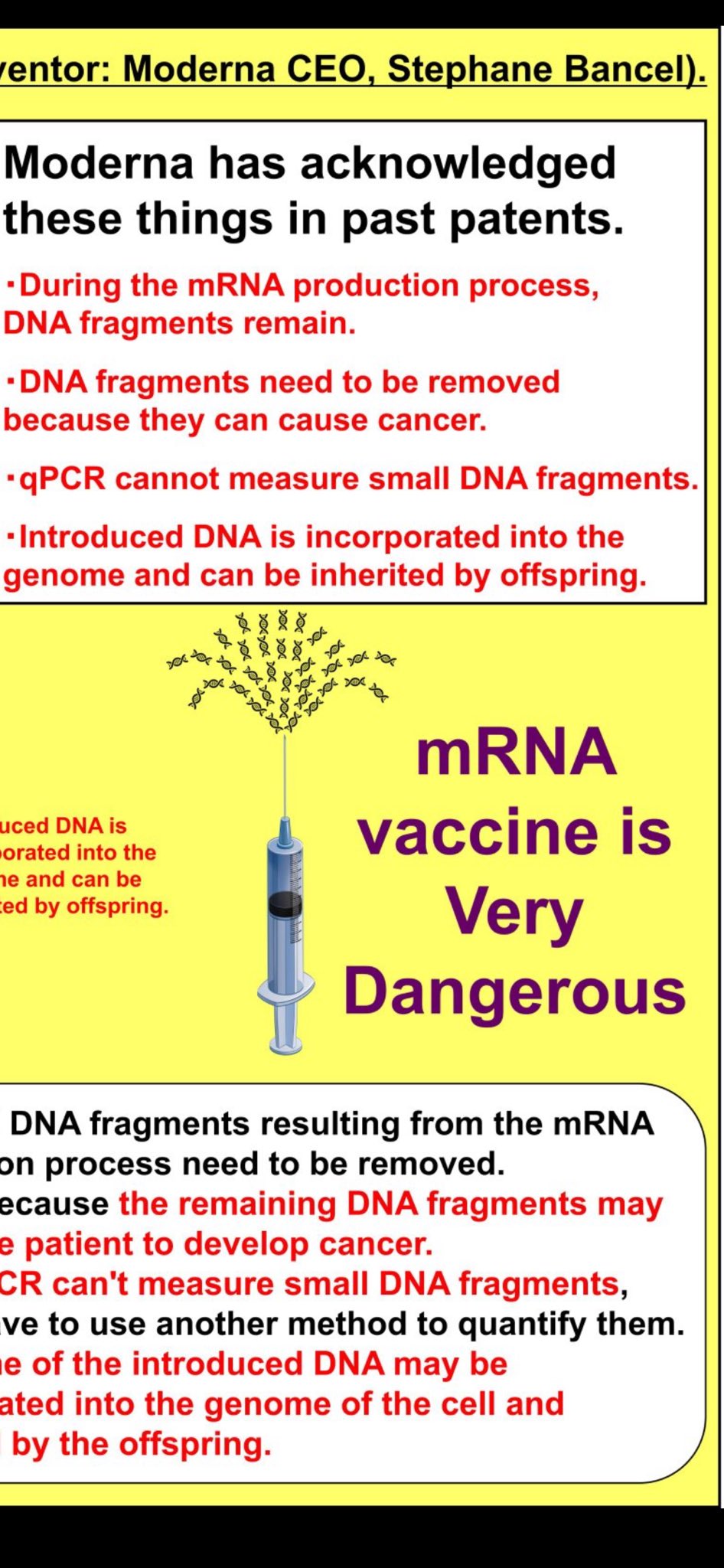

These admissions demonstrate that DNA contamination risks were well-understood, documented, and explicitly warned against in manufacturer's own patent filings years before the pandemic vaccine rollout.
Why This Knowledge Matters
These patent statements reveal that:
- Manufacturers knew DNA contamination was a potential problem
- They understood the theoretical cancer risks
- They acknowledged limitations of standard testing methods
- They recognized the possibility of genomic integration
The Timing Issue
These patent applications were filed years before the COVID-19 pandemic. This means manufacturers:
- Had prior knowledge of DNA contamination risks in mRNA technology
- Understood the need for specialized testing beyond standard qPCR methods
- Were aware of theoretical safety concerns including cancer risks
- Did not disclose these risks to the public during vaccine rollout
Biological Risk Assessment: Beyond Theoretical Concerns
Established Risk Mechanisms
- Genomic Integration: Foreign DNA incorporation with potential oncogene activation
- Promoter-Driven Expression: SV40 enhancer activating nearby genes
- Inflammatory Response: Foreign DNA triggering immune reactions via cGAS-STING
Newly Identified Threat
- Somatic Hypermutation Disruption: SV40 targeting of AID enzyme and antibody diversity machinery
Evidence Status
- In Vitro Confirmation: Multiple studies show SV40 promoter activity and DNA presence
- In Vivo Gap: No demonstrated integration or clinical sequelae in vaccinated populations
- Biological Plausibility: Multiple identified mechanisms with historical precedent
 Source: McKernan et al., Nanopore sequencing (2025) - Coverage map showing DNA fragments mapping to spike ORF and SV40 promoter/enhancer regions in vaccine samples
Source: McKernan et al., Nanopore sequencing (2025) - Coverage map showing DNA fragments mapping to spike ORF and SV40 promoter/enhancer regions in vaccine samples
Understanding the Biological Mechanisms
To understand why DNA contamination in vaccines matters, we need to explore several biological mechanisms that researchers have investigated.

⚠️ VISUAL EVIDENCE NOTE: This microscopic image demonstrates the direct cellular uptake and nuclear localization of fluorescently labeled DNA contaminants from mRNA vaccines, providing physical evidence of intracellular penetration and nuclear access—exactly the pathways required for genomic integration events.
Can mRNA Integrate Into Human DNA?
For decades, the conventional understanding was that mRNA vaccines couldn't integrate into human DNA because mRNA is temporary and doesn't enter the cell nucleus. However, recent research has challenged this assumption.
Key Study: In 2022, Aldén et al. published findings that BNT162b2 mRNA could be reverse-transcribed into DNA in human liver cells (Current Issues in Molecular Biology).
What This Means:
- Reverse transcription is the process where RNA is converted back into DNA
- This can occur through natural enzymes like LINE-1 retrotransposons that exist in human cells
- If mRNA can be converted to DNA, it raises questions about whether DNA contamination could integrate into the genome
- This challenges the long-standing assumption that mRNA vaccines cannot affect human DNA
Immune System Changes
Researchers have documented several unexpected immunological effects following mRNA vaccination:
IgG4 Class Switching:
- A 2023 study by Irrgang et al. found that repeated mRNA vaccination causes the immune system to shift toward producing IgG4 antibodies (PubMed)
- IgG4 antibodies are typically less inflammatory and less effective at fighting infections
- This class switching is unusual and its long-term implications are not fully understood
Spike Protein Persistence:
- Patterson et al. detected SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in immune cells up to 15 months after infection (Frontiers in Immunology)
- While this study focused on natural infection, it raises questions about how long vaccine-produced spike protein might persist
Medical Findings After Vaccination
Several published autopsy studies have reported unusual findings after mRNA vaccination:
Brain Inflammation:
- Mörz (2022) documented multifocal necrotizing encephalitis (brain inflammation) following BNT162b2 vaccination (Vaccines)
Heart Muscle Damage:
- Schwab et al. characterized myocarditis pathology following vaccination (PMC)
Young Adult Deaths:
- Gill et al. reported autopsy findings in two teenagers who died after Pfizer vaccination (Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine - Archived)
Important Scientific Context
It's crucial to understand that:
- Correlation vs. Causation: These findings don't prove that DNA contamination caused these outcomes
- Individual Cases: Autopsy reports typically involve individual cases, which may not represent population-level effects
- Alternative Explanations: Other factors could contribute to these observed effects
- Research Ongoing: The scientific community is still investigating these mechanisms
The Fundamental Question
The presence of DNA contamination - especially with SV40 enhancer sequences - raises legitimate scientific questions about:
- Could this contribute to unexpected biological effects?
- Were these possibilities adequately investigated before widespread use?
- Does the presence of biologically active genetic material change the safety profile?
These are legitimate scientific questions that deserve thorough, independent investigation.
Regulatory Standards vs Reality
Established Safety Benchmarks
- WHO TRS 978 Annex 3: ≤10 ng residual DNA per dose with <200 bp fragmentation
- ICH Q5D/Q6B: Validated purification and risk assessment requirements
- Historical Context: Standards developed from gene therapy and viral vector experience
The Transparency Gap
- Regulator Statements: Health Canada, EMA, and FDA maintain authorized lots meet specifications
- Missing Data: No public release of raw lot testing data or comprehensive comparability studies
- Independent Verification: No GMP-grade replication despite multiple lab confirmations
Critical Unresolved Questions
- Dose-Response Relationship: Do higher DNA levels correlate with adverse events?
- Lot Variability: Why do some lots show minimal contamination while others exceed limits 500-fold?
- Biodistribution: Where does plasmid DNA travel and for how long?
- Clinical Impact: Are there population-level health effects from DNA contamination?
- Regulatory Justification: What specific data supports the "minimal risk" determination?
Moving Forward: What Should Happen Next
Immediate Needs
- Full Data Transparency: Release all manufacturing quality control and comparability data
- Multi-Laboratory Audit: GMP-grade independent testing of retained lots
- Clinical Correlation: Examine adverse events by manufacturing lot and DNA levels
Long-Term Solutions
- Regulatory Reform: Emergency use products should match conventional medicine quality standards
- Independent Oversight: Separate safety monitoring from promotional review
- Manufacturing Standards: Updated guidelines for mRNA product purity and characterization
Related Investigations
For readers seeking additional context and deeper analysis:
The Stability Trap: How mRNA Vaccine Engineering and DNA Contamination Created a Perfect Storm Analysis of how mRNA stability modifications intersect with DNA contamination to create biological risks.
DNA Contamination & mRNA Vaccine Biology: Curated Reference Roadmap Comprehensive reference database with primary sources, regulatory documents, and scientific studies.
Pfizer Process 1 vs Process 2: What Changed, What's Measured, and What Remains Uncertain Detailed investigation into manufacturing changes between clinical trial and commercial vaccine lots.
Conclusion: From Quality Control Failure to Public Health Concern
The SV40 DNA contamination story represents a cascade of failures:
- Manufacturing Control Failure: Unexpected SV40 sequences in final products
- Regulatory Transparency Failure: Internal alarm without public disclosure
- Scientific Integrity Failure: Removal of planned safety comparisons
- Corporate Accountability Failure: Prior knowledge of risks without adequate mitigation
What began as a quality control issue has evolved into a complex public health concern involving:
- Demonstrated manufacturing inconsistencies
- Identified biological mechanisms of potential harm
- Systematic lack of transparency
- Global scientific consensus on contamination
As one researcher noted: "We're finding things that, according to official specifications, shouldn't be there. The question has shifted from whether contamination exists to whether it matters for human health."
The burden of proof now rests with manufacturers and regulators to demonstrate that these findings—confirmed across eight independent laboratories and supported by identified biological mechanisms—truly represent "minimal risk" to public health.
Key References
RNA:DNA Hybrid Mechanism:
- Sutton RE, et al. "Specificity of the nick-closing activity of bacteriophage T4 DNA ligase." Gene. 1997;200(1-2):233-245. PMID: 9345303. (Demonstrates 100-fold reduction in DNase I activity on RNA:DNA hybrids)
DNA Contamination Studies:
- McKernan K, et al. "RNA:DNA hybrids survive digestion in mRNA vaccine manufacturing." Zenodo. 2025. doi:10.5281/zenodo.17832183
- Speicher DJ, Rose J, McKernan K, et al. "Quantification of residual plasmid DNA and SV40 promoter in COVID-19 vaccines." Immunological Investigations. 2025;54(1):2551517. DOI: 10.1080/08916934.2025.2551517
Regulatory Documents:
- EMA Assessment Report REC 027 (2021). Required DNase stability studies.
- Health Canada FOI emails (2023). SV40 contamination internal communications.
This investigation continues because independent scientists, journalists, and concerned citizens refuse to accept "trust us" as adequate scientific evidence for products administered to billions of people.